Navigating the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Marine Wire Size and Ampacity
Published by Aaron Swift on Nov 14th 2024
Understanding Marine Wire Size and Ampacity: A Guide for Boaters
Whether you're a seasoned sailor or a novice on the open waters, grasping the intricacies of marine wire size and ampacity is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of your vessel. From powering navigation lights to running advanced electronics, the electrical systems on boats require careful consideration to prevent potential hazards and ensure seamless operation.
Introduction to Marine Wire Sizing
The Basics of Marine Wire
Marine wires differ significantly from standard land-based wiring due to their exposure to harsher environmental conditions, including saltwater, humidity, and constant motion. Specifically designed to resist corrosion and degradation, marine wires are well-suited for the demanding conditions of the open sea. They typically feature additional insulation layers and are constructed from materials engineered to withstand the corrosive effects of saltwater.
Wire Gauge and Ampacity
One of the foundational aspects of marine wiring is wire gauge, which denotes the thickness of the wire. The gauge directly influences ampacity—the maximum current a wire can safely carry. Choosing the appropriate wire gauge is essential to ensure the safety and efficiency of your boat's electrical system. A wire that is too small can lead to overheating and fire hazards, while one that is excessively large may add unnecessary weight and cost.
Factors Influencing Marine Wire Size and Ampacity
Voltage Drop
Maintaining an appropriate voltage level is essential for the proper functioning of marine electronics. Voltage drop, caused by the resistance in the wire, can diminish performance and potentially damage sensitive equipment. Selecting the correct wire gauge helps minimize voltage drop, ensuring that power reaches its destination with minimal loss.
Length of the Wire Run
The distance between the power source and the device affects wire resistance. Longer wire runs have higher resistance, impacting the overall ampacity of the system. Understanding the length of your wire runs is crucial for selecting the right wire gauge.
Type of Load
Different marine devices and equipment have varying ampacity requirements. High-amperage devices, such as windlasses or electric winches, require thicker wires to handle the increased current flow without overheating.
Determining the Right Wire Gauge for Your Boat
Marine Wire Size and Ampacity Charts

Marine wire size and ampacity charts are valuable tools for selecting the appropriate wire gauge. These charts consider voltage, wire length, and load type to recommend the optimal wire gauge for specific applications.
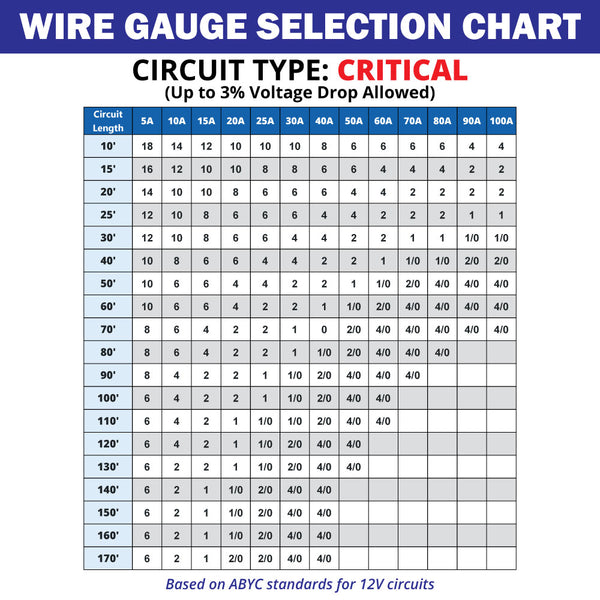
Consult Manufacturer Guidelines
Manufacturers of marine equipment typically provide guidelines regarding recommended wire sizes for their products. Adhering to these recommendations ensures compatibility and optimal performance.
Ensuring Electrical Safety on Your Boat
Regular Inspections
Preventive measures are vital for maintaining the safety of your boat's electrical system. Regular inspections of wiring for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage can help identify potential issues before they escalate.
Use Marine-Grade Components
Choosing marine-grade electrical components is essential for the longevity and reliability of your boat's electrical system. From connectors to switches, selecting components designed for the marine environment helps prevent corrosion and ensures seamless operation.
Common Marine Wire Size and Ampacity Guidelines
General Lighting Circuits
For general lighting circuits on a boat, where the ampacity requirements are relatively low, a 16 or 18-gauge marine wire is typically sufficient. These circuits usually power navigation lights, cabin lights, and other low-current devices.
Powering Electronics
Electronics such as chartplotters, radars, and GPS systems may require higher ampacity. A 14 or 12-gauge marine wire is commonly recommended for these applications to handle increased current flow.
High-Amperage Devices
Devices with high amperage requirements, such as windlasses and electric winches, demand thicker wires. A 10 or 8-gauge marine wire is often suitable for these applications to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Conclusion: Navigating Smooth Seas with Proper Marine Wire Size
In the vast expanse of the open sea, where the elements can be unforgiving, ensuring the reliability and safety of your boat's electrical system is paramount. By understanding marine wire size and ampacity and following best practices, you can enhance the performance of your vessel while mitigating the risks associated with electrical issues.
Remember to consult marine wire size and ampacity charts, adhere to manufacturer guidelines, and conduct regular inspections to keep your boat's electrical system in excellent condition. Investing time and effort in selecting the right wire gauge and maintaining a robust electrical system will undoubtedly contribute to smooth sailing on your maritime adventures.


